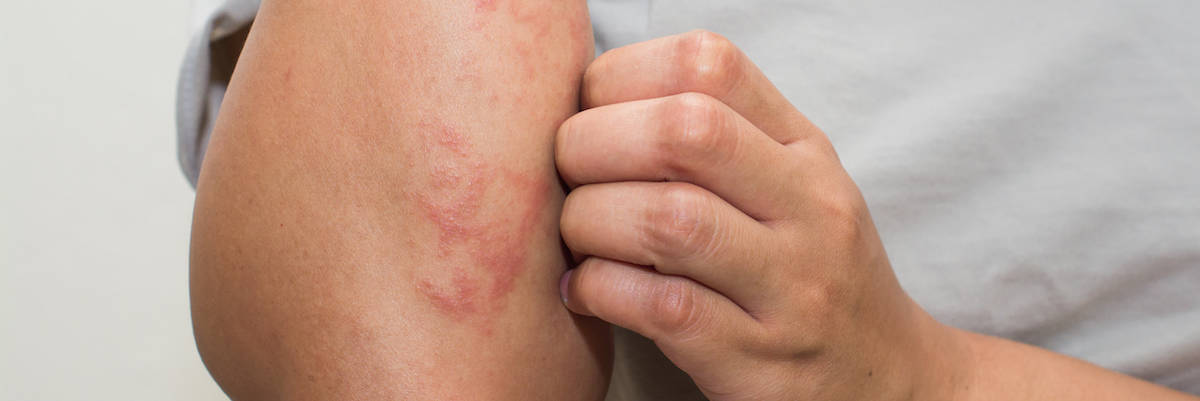
Psoriasis is a common skin condition that is caused by an autoimmune response. The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but researchers believe it is due to a person’s genetics or environmental triggers, including infections and stress. It is considered a chronic disease, although it may come and go throughout a person’s life.
The main symptom of Psoriasis are red plaque-like areas or silvery, scaly areas of skin on a person’s body. Psoriasis plaques are caused by skin cells that multiple and rapidly build up. These cells grow at a five-time faster rate than normal skin cells. These cells eventually begin to pile on top of each other, which causes the appearance of the scales or plaques. Patches of psoriasis may itch, burn, or become very dry and cracked.
There are multiple types of psoriasis including:
- Plaque Psoriasis: This is the most common form of psoriasis and causes itchy, red scaly patches.
- Nail Psoriasis: This type of psoriasis affects the nails, fingernails and toenails, causing pitting and discoloration.
- Guttate Psoriasis: This type is usually triggered by a bacterial infection and can be characterized by fine scales on your arms, legs, and scalp.
- Inverse Psoriasis: This type affects areas such as groin, under breasts, and around genitals.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: This type of psoriasis is characterized by scaly skin and swollen joints.
If you have a family member or friend with psoriasis, it is important to know that is not contagious and cannot be transmitted to another person. Oftentimes, people who have diseases such as diabetes, Crohn’s disease, or other autoimmune disorders will also have psoriasis. It is not quite understood what the link is, other than it appears to be related to disorders and diseases that produce an overactive immune response.
While there is no cure for psoriasis, there are treatments available that can help with the symptoms of psoriasis. Your dermatologist can assess what type of psoriasis you have and then development a treatment plan that works for you. Topical treatments that may give you relief include topical corticosteroids, as they help reduce inflammation and itching. To slow skin growth, some psoriasis sufferers have found that Vitamin D helps with this issue. There are a few other topical creams that can be prescribed by a dermatologist to help slow skin cell growth and remove scales to make skin smoother. If topical treatments do not work, your dermatologist may recommend phototherapy (light therapy). UVB Phototherapy has been found to help reduce the symptoms of psoriasis.
If you are suffering from psoriasis, please call our office to schedule an appointment with a Dermatologist who can help alleviate you from your troublesome symptoms. We also offer clinical trials for psoriasis suffers. To learn more, visit our clinical trials page here.
Disclaimer: This blog provides general information and discussion about medical, cosmetic, mohs, and surgical dermatology. The words and other content provided in this blog, and in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice. If the reader or any other person has a medical concern, he or she should consult with an appropriately-licensed dermatologist or other health care worker.